Types of 3D printer
Fused deposition modeling (FDM)
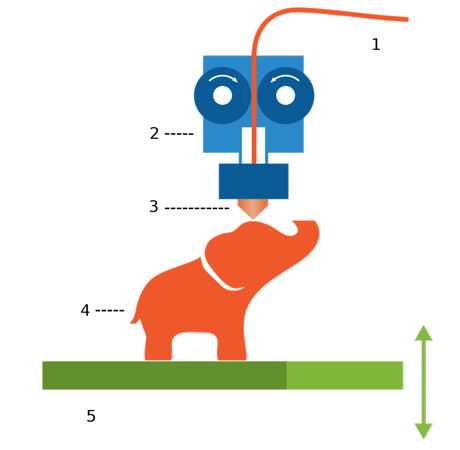
3D printers which use FDM Technology construct objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament. The whole process is somewhat similar to stereolithography. Specialized programs or Slicers "cut" CAD models into layers and computes the manner printer's extruder would assemble each layer.
Stereolithography(SLA)
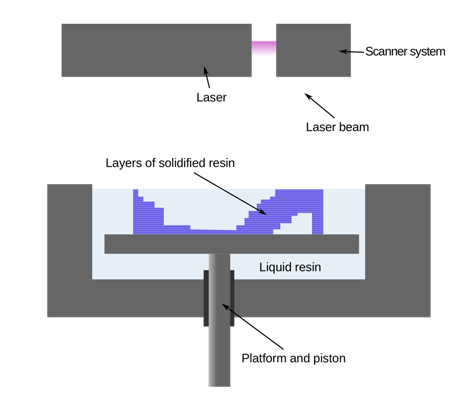
SLA 3D printers operate with an excess of liquid plastic that after a while hardens and forms to a solid object.After the plastic hardens a stage of the printer drops down in the tank a fraction of a millimeter and laser forms another layer until printing is finished. After all, layers are printed, the item has to be rinsed using a solvent and then put in an ultraviolet oven to complete processing.
Digital Light Processing(DLP)
For 3D printing, both DLP and SLA functions with photopolymers. However, the difference between SLA and DLP technology is that DLA requires an additional source of lighting. 3D printing amateurs frequently use more traditional sources of lights like arc lamps for DLP printing. The other important piece of the DLP puzzle is an LCD (liquid crystal display) panel, which gets applied to the entire surface of the 3D printed layer during a single run of the DLP procedure. The substance used for printing is a liquid plastic resin that's set in a transparent resin container. The resin hardens quickly when exposed to a lot of photons, or more simply put, bright light. The printing speed for DLP is the kicker. A layer of hardened material can be produced with this kind of printer in few seconds. After the layer is completed, it is transferred, and printing of the next layer is started.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
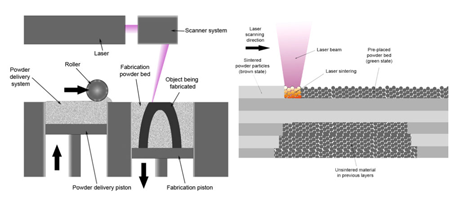
The most notable difference between SLS and SLA is that it uses powdered material in the vat rather than liquid resin in a cube, like SLS does.Unlike some other additive production processes, such as FDM and SLA, SLS does not have to use some other support structures as the object being printed is surrounded by unsintered powder.
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Through the last two decades, these technologies have either fallen out of fashion or proved to be economically unviable.
Laminated object manufacturing (LOM)
Through the last two decades, these technologies have either fallen out of fashion or proved to be economically unviable.
Digital Beam Melting (EBM)
Through the last two decades, these technologies have either fallen out of fashion or proved to be economically unviable.
